
Professor Nicolas Locker
About
Biography
After studying Biochemistry as an undergraduate, I dived into the exciting world of RNA-protein interactions, first through an MSc in Molecular Biophysics at University Paris VI (Fr), then during my PhD with Eric Guittet at the Institut de Chimie des Substances Naturelles and University Paris XI (Fr) graduating in 2003. During this time, I applied NMR spectroscopy and biochemical techniques to characterise RNA-proteins interactions important for HIV replication. This got me interested into the role of RNA structure in viral life cycle. I pursued this interest at the Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Cambridge (UK), with Peter Lukavsky, teasing out how structures within the HCV RNA coordinates the recruitment of the translation machinery by isolating ribosomal complexes. At University Paris Descartes (Fr), with Bruno Sargueil, I then established a new mechanism used by HIV to recruit several ribosomes and synthesise viral proteins.
In 2009, I established my own lab at University of Surrey, first as Lecturer, Senior Lecturer, Reader and now Professor of Virology and Lead for the Virology Section. Our team specialises in the control of gene expression by viruses, characterising how viruses hijack the translational machinery to make their own proteins, but also how they manipulate gene expression in the infected host. Building on this, we now also study mechanisms of translational control important in health and diseases.
Areas of specialism
University roles and responsibilities
- Module Coordinator for BMS3079 Human Microbial Diseases
- Module Coordinator for MMIM015 Viral infections
- Virology Section Lead
- Chair of the Board of Examiners for the M.Sc in Veterinary Microbiology
- Member of the University Staff Survey Central Action Group
- Student-Staff Liaison Committee coordinator for Level 5
- Academic Integrity Officer
My qualifications
Affiliations and memberships
News
ResearchResearch interests
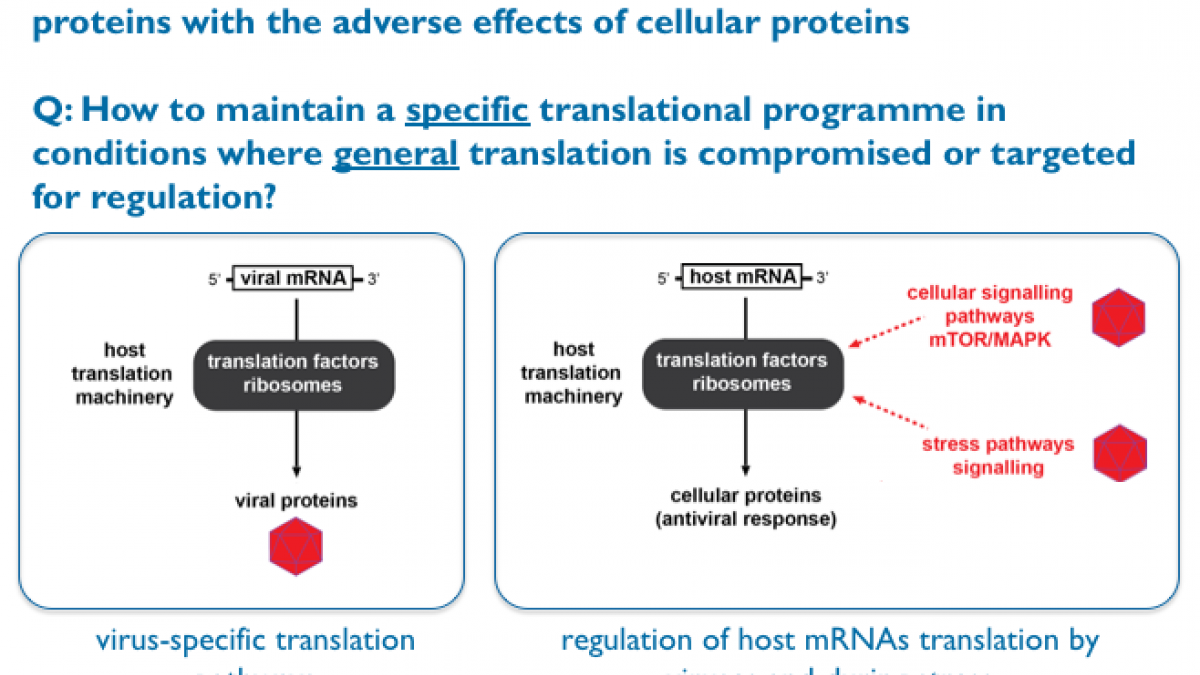
While we ask diverse research questions in the Locker lab, they all converge towards one over-arching theme: How do cells or pathogens maintain a specific translational programme in conditions where general translation is compromised or targeted for regulation?
Our main research interests are the regulation of gene expression and translational control during viral infection. We are trying to address fundamental questions at the interface between microbiology and RNA biology by asking how microbial genomes take control of the infected host protein synthesis machinery and how this impacts on the host translational landscape at the molecular and cellular level. We are also interested in other translational control mechanisms that impact on heath and diseases.
Research projects
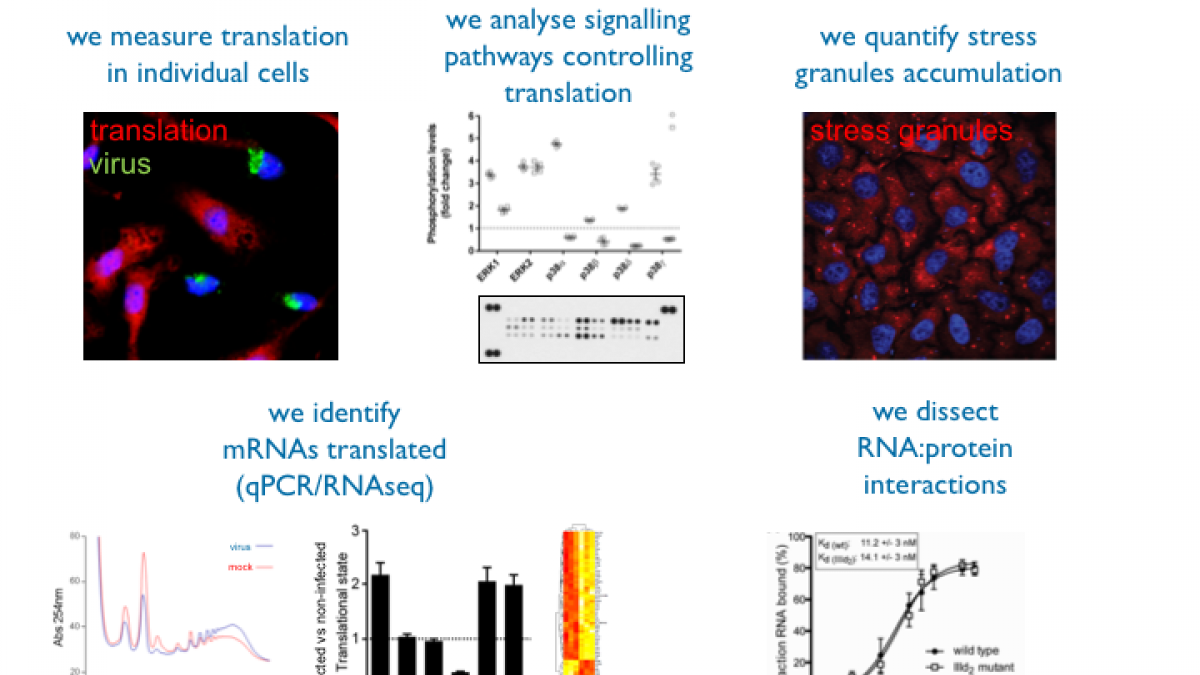
Based on previous experience about translational control mediated by viral RNAs, our goal is to dissect host—pathogen interactions and understand translational control during norovirus infection. Human norovirus (HuNV) is a member of the calicivirus family and is a major cause of viral gastroenteritis. Norovirus lacks a suitable cell culture system, so its replication mechanisms are poorly understood, but two animal caliciviruses, the feline calicivirus (FCV) and mouse norovirus (MNV) provide models to increase our understanding of norovirus translation and replication. Unlike cellular mRNAs, the calicivirus RNA genome does not possess a 5' cap structure but instead has a 13–15 kDa viral protein, genome linked (VPg) directing translation and hijacking the host protein synthesis machinery. Previous work from the Roberts (Surrey) and Goodfellow (University of Cambridge) demonstrated that VPg acts as a novel proteinaceous ‘cap substitute’ and interacts with eIF4E (the cap-binding protein), eIF4G and eIF4A (Goodfellow et al. 2005, Chaudhry et al. 2006), while it is known that the eIF4E phosphorylation and availability is subject to fine regulation during viral infection (Mohr et al. 2011), either to control the host antiviral response or to promote viral translation. Therefore, supported by the BBSRC, we investigate how caliciviruses modulate the host protein synthesis machinery, especially eIF4E and 4E-BP1, the cell signalling pathways involved in this process, and the effect on host and viral mRNA translation. We use RNA-seq approaches to understand these changes on a genome-wide level. To deepen our knowledge of modulation of mRNA metabolism by viruses we are also studying how Stress Granules and P-bodies, which are sites of mRNA storage and degradation respectively, are affected during viral infection. In collaboration with the Ruggieri lab in Heidelberg, we address links between translational control and stress responses using flaviviruses such as Dengue virus as models.
These projects are led by Dr Michele Brocard, Dr Valentina Iadevaia and Glenys Lewis. Michele has a wealth of experience in RNA biology and translational control mechanisms following her time as post-doc in the labs of Simon Morley and then Michelle West at Sussex. Valentina adds her experience in cellular signalling pathways that control translation gained while working with Chris Proud at Southampton and in the function of RNA-binding protein with Andre Gerber at Surrey. Glenys currently works towards obtaining her MSc Medical Microbiology and studies stress granules function.
Role of Internal ribosome entry sites (IRES) during viral translationTo better understand the role of specific viral RNA domains during translation and the regulation of their activities we are dissecting the structure-function relationship of several viral IRESes. In collaboration between Dr Locker, Prof Roberts (Surrey) and Prof Belsham (DTU National Veterinary Institute, Denmark) we investigate the role of HCV-like IRES elements of Seneca Valley Virus (SVV) and classical swine fever virus (CSFV) infection. In collaboration with Prof Shih (Chang Gung University Taiwan) we study how cellular proteins can assist viral IRES RNAs in the takeover of the virus-infected cell translation machinery during enterovirus 71 (EV71) infection. We are also characterizing a new IRES element directing the synthesis of vFLIP, a key tumorigenesis factor during Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) infection.
Dr Nicolas Locker and Dr Margaret Carter (lab manager) both drive these highly collaborative projects. We are experienced in reconstituting and characterising RNA-protein interactions driving the assembly of ribosomal complexes using purified native translation factors. Margaret also brings her expertise in using cell culture assays to study viral replication.
Lab membersDr Margaret Carter (Lab manager)
Dr Michele Brocard (postdoc, BBSRC-funded)
Dr Valentina Iadevaia (postdoc, BBSRC-funded)
Matthew Brownsword (PhD student, shared with The Pirbright Institute)
Glenys Lewis (M.Sc student, Medical Microbiology)
Research collaborations
- Prof Goodfellow, University of Cambridge UK
- Dr Ruggieri, University of Heidelberg DE
- Dr Sargueil, Université Paris Descartes, FR
- Prof Roy Parker, University of Colorado, USA
- Dr Peter McCormick, Queen Mary University London, UK
- Prof Belsham, DTU National Veterinary Institute, DK
- Dr Carl Ernst, McGill University, CA
- Dr Stephane Lefrancois, Laval University, CA
- Prof Andrew Ewing, University of Gotenburg, SE
- Prof Andreas Schuppert, University of Aachen, DE

Research interests
While we ask diverse research questions in the Locker lab, they all converge towards one over-arching theme: How do cells or pathogens maintain a specific translational programme in conditions where general translation is compromised or targeted for regulation?
Our main research interests are the regulation of gene expression and translational control during viral infection. We are trying to address fundamental questions at the interface between microbiology and RNA biology by asking how microbial genomes take control of the infected host protein synthesis machinery and how this impacts on the host translational landscape at the molecular and cellular level. We are also interested in other translational control mechanisms that impact on heath and diseases.
Research projects
Based on previous experience about translational control mediated by viral RNAs, our goal is to dissect host—pathogen interactions and understand translational control during norovirus infection. Human norovirus (HuNV) is a member of the calicivirus family and is a major cause of viral gastroenteritis. Norovirus lacks a suitable cell culture system, so its replication mechanisms are poorly understood, but two animal caliciviruses, the feline calicivirus (FCV) and mouse norovirus (MNV) provide models to increase our understanding of norovirus translation and replication. Unlike cellular mRNAs, the calicivirus RNA genome does not possess a 5' cap structure but instead has a 13–15 kDa viral protein, genome linked (VPg) directing translation and hijacking the host protein synthesis machinery. Previous work from the Roberts (Surrey) and Goodfellow (University of Cambridge) demonstrated that VPg acts as a novel proteinaceous ‘cap substitute’ and interacts with eIF4E (the cap-binding protein), eIF4G and eIF4A (Goodfellow et al. 2005, Chaudhry et al. 2006), while it is known that the eIF4E phosphorylation and availability is subject to fine regulation during viral infection (Mohr et al. 2011), either to control the host antiviral response or to promote viral translation. Therefore, supported by the BBSRC, we investigate how caliciviruses modulate the host protein synthesis machinery, especially eIF4E and 4E-BP1, the cell signalling pathways involved in this process, and the effect on host and viral mRNA translation. We use RNA-seq approaches to understand these changes on a genome-wide level. To deepen our knowledge of modulation of mRNA metabolism by viruses we are also studying how Stress Granules and P-bodies, which are sites of mRNA storage and degradation respectively, are affected during viral infection. In collaboration with the Ruggieri lab in Heidelberg, we address links between translational control and stress responses using flaviviruses such as Dengue virus as models.
These projects are led by Dr Michele Brocard, Dr Valentina Iadevaia and Glenys Lewis. Michele has a wealth of experience in RNA biology and translational control mechanisms following her time as post-doc in the labs of Simon Morley and then Michelle West at Sussex. Valentina adds her experience in cellular signalling pathways that control translation gained while working with Chris Proud at Southampton and in the function of RNA-binding protein with Andre Gerber at Surrey. Glenys currently works towards obtaining her MSc Medical Microbiology and studies stress granules function.
To better understand the role of specific viral RNA domains during translation and the regulation of their activities we are dissecting the structure-function relationship of several viral IRESes. In collaboration between Dr Locker, Prof Roberts (Surrey) and Prof Belsham (DTU National Veterinary Institute, Denmark) we investigate the role of HCV-like IRES elements of Seneca Valley Virus (SVV) and classical swine fever virus (CSFV) infection. In collaboration with Prof Shih (Chang Gung University Taiwan) we study how cellular proteins can assist viral IRES RNAs in the takeover of the virus-infected cell translation machinery during enterovirus 71 (EV71) infection. We are also characterizing a new IRES element directing the synthesis of vFLIP, a key tumorigenesis factor during Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) infection.
Dr Nicolas Locker and Dr Margaret Carter (lab manager) both drive these highly collaborative projects. We are experienced in reconstituting and characterising RNA-protein interactions driving the assembly of ribosomal complexes using purified native translation factors. Margaret also brings her expertise in using cell culture assays to study viral replication.
Dr Margaret Carter (Lab manager)
Dr Michele Brocard (postdoc, BBSRC-funded)
Dr Valentina Iadevaia (postdoc, BBSRC-funded)
Matthew Brownsword (PhD student, shared with The Pirbright Institute)
Glenys Lewis (M.Sc student, Medical Microbiology)
Research collaborations
- Prof Goodfellow, University of Cambridge UK
- Dr Ruggieri, University of Heidelberg DE
- Dr Sargueil, Université Paris Descartes, FR
- Prof Roy Parker, University of Colorado, USA
- Dr Peter McCormick, Queen Mary University London, UK
- Prof Belsham, DTU National Veterinary Institute, DK
- Dr Carl Ernst, McGill University, CA
- Dr Stephane Lefrancois, Laval University, CA
- Prof Andrew Ewing, University of Gotenburg, SE
- Prof Andreas Schuppert, University of Aachen, DE




Supervision
Postgraduate research supervision
Matthew Brownsword (Ph.D student with TPI)
Glenys Lewis (M.Sc Medical Microbiology)
Completed postgraduate research projects I have supervised
Majid Al-Sailawi (Ph.D student)
Melvin Leteane (Ph.D student)
David Taylor (Ph.D student)
Mariam Sulaiman (Ph.D student)
Nefeli Karataraki (M.Sc Medical Microbiology)
Aimilios Simoudis (M.Sc Medical Microbiology)
Hanan Al-Busaidi (M.Sc Medical Microbiology)
Teaching
I teach virology and molecular biology on several modules across a wide range of programmes from first year B.Sc to M.Sc.This includes BMS1026: Microbiology; BMS2037: Cellular Microbiology and Virology; BMS2036: Molecular Biology and Genetics 2; BMS3079: Human Microbial Diseases (Coordinator); BMS3073: Epidemiology, Control and Treatment of Infectious Disease; MMIM015: Viral Infections (Coordinator); MMIM018: Microbial Genetics and Molecular Biology; MMVM007: Diseases of Animal Systems: Gastrointestinal Diseases of Animals; MMVM009: Diseases of Animal Systems: Systems Diseases of Animals
Publications
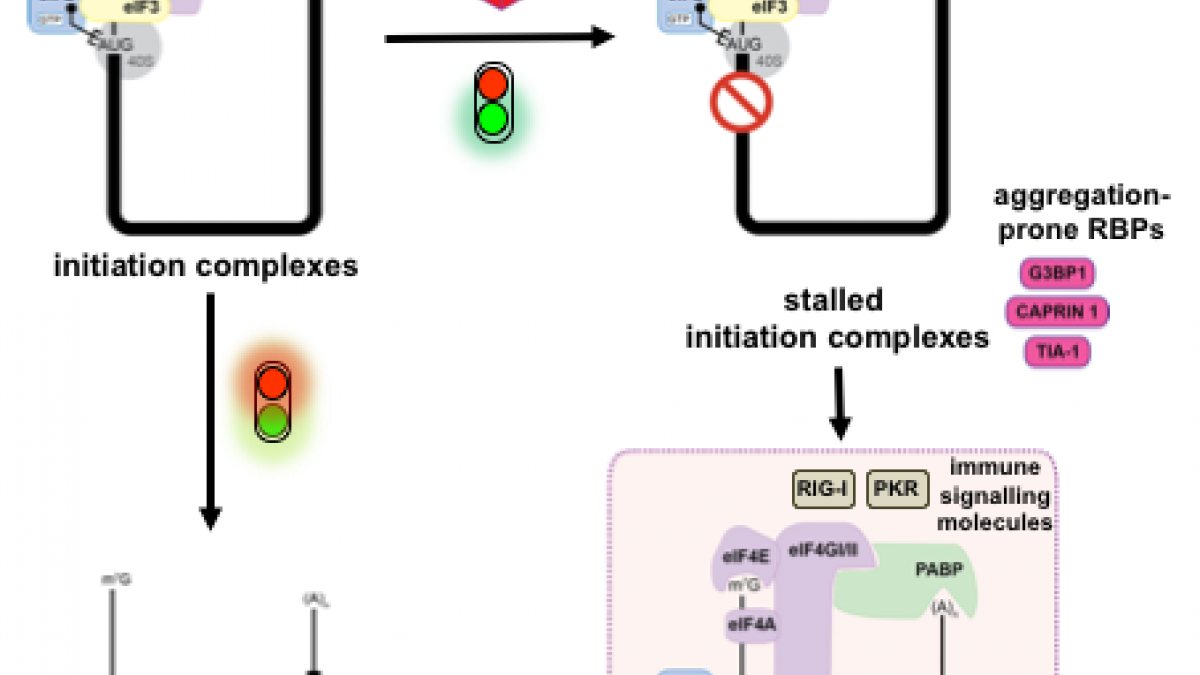
The assembly of membrane-less organelles such as stress granules (SGs) is emerging as central in helping cells rapidly respond and adapt to stress. Following stress sensing, the resulting global translational shutoff leads to the condensation of stalled mRNAs and proteins into SGs. By reorganising cytoplasmic contents, SGs can modulate RNA translation, biochemical reactions and signalling cascades to promote survival until the stress is resolved. While mechanisms for SG disassembly are not widely understood, the resolution of SGs is important for maintaining cell viability and protein homeostasis. Mutations that lead to persistent or aberrant SGs are increasingly associated with neuropathology and a hallmark of several neurodegenerative diseases. Mutations in CLN3 are causative of juvenile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (JNCL), a rare neurodegenerative disease affecting children also known as Batten disease. CLN3 encodes a transmembrane lysosomal protein implicated in autophagy, endosomal trafficking, metabolism, and response to oxidative stress. Using a HeLa cell model lacking CLN3, we now show that CLN3KO is associated with an altered metabolic profile, reduced global translation, and altered stress signalling. Furthermore, loss of CLN3 function results in perturbations in SG dynamics, resulting in assembly and disassembly defects, and altered expression of the key SG nucleating factor G3BP1. With a growing interest in SG-modulating drugs for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, novel insights into the molecular basis of CLN3 Batten disease may reveal avenues for disease-modifying treatments for this debilitating childhood disease.
Recent exciting studies have uncovered how membrane-less organelles, also known as biocondensates, are providing cells with rapid response pathways, allowing them to re-organise their cellular contents and adapt to stressful conditions. Their assembly is driven by the phase separation of their RNAs and intrinsically disordered protein components into condensed foci. Among these, stress granules are dynamic cytoplasmic biocondensates that form in response to many stresses, including activation of the integrated stress response or viral infections. Stress granules sit at the crossroads between antiviral signalling and translation because they concentrate signalling proteins and components of the innate immune response, in addition to translation machinery and stalled mRNAs. Consequently, they have been proposed to contribute to antiviral activities, and therefore are targeted by viral countermeasures. Equally, stress granules components can be commandeered by viruses for their own efficient replication. Phase separation processes are an important component of the viral life cycle, for example driving assembly of replication factories or inclusion bodies. Therefore, in this review we will outline the recent understanding of this complex interplay and tug of war between viruses, stress granules and their components.
To rapidly adapt to stresses such as infections, cells have evolved several mechanisms, which include the activation of stress response pathways and the innate immune response. These stress responses result in the rapid inhibition of translation and condensation of stalled mRNAs with RNA-binding proteins and signalling components into cytoplasmic biocondensates called stress granules (SGs). Increasing evidence suggests that SGs contribute to antiviral defence, and thus viruses need to evade these responses to propagate. We previously showed that feline calicivirus (FCV) impairs SG assembly by cleaving the scaffolding protein G3BP1. We also observed that uninfected bystander cells assembled G3BP1-positive granules, suggesting a paracrine response triggered by infection. We now present evidence that virus-free supernatant generated from infected cells can induce the formation of SG-like foci, which we name paracrine granules. They are linked to antiviral activity and exhibit specific kinetics of assembly-disassembly, and protein and RNA composition that are different from canonical SGs. We propose that this paracrine induction reflects a novel cellular defence mechanism to limit viral propagation and promote stress responses in bystander cells.
To rapidly adapt to harmful changes to their environment, cells activate the integrated stress response (ISR). This results in an adaptive transcriptional and translational rewiring, and the formation of biomolecular condensates named stress granules (SGs), to resolve stress. In addition to this first line of defence, the mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt) activates a specific transcriptional programme to maintain mitochondrial homeostasis. We present evidence that SGs and UPRmt pathways are intertwined and communicate. UPRmt induction results in eIF2a phosphorylation and the initial and transient formation of SGs, which subsequently disassemble. The induction of GADD34 during late UPRmt protects cells from prolonged stress by impairing further assembly of SGs. Furthermore, mitochondrial functions and cellular survival are enhanced during UPRmt activation when SGs are absent, suggesting that UPRmt-induced SGs have an adverse effect on mitochondrial homeostasis. These findings point to a novel crosstalk between SGs and the UPRmt that may contribute to restoring mitochondrial functions under stressful conditions.
Several cellular pathways contribute to neurodegenerative tauopathy-related disorders. Microglial activation, a major component of neuroinflammation, is an early pathological hallmark that correlates with cognitive decline, while the unfolded protein response (UPR) contributes to synaptic pathology. Sleep disturbances are prevalent in tauopathies and may also contribute to disease progression. Few studies have investigated whether manipulations of sleep influence cellular pathological and behavioural features of tauopathy. We investigated whether trazodone, a licensed antidepressant with hypnotic efficacy in dementia, can reduce disease-related cellular pathways and improve memory and sleep in male rTg4510 mice with a tauopathy-like phenotype. In a 9-week dosing regimen, trazodone decreased microglial NLRP3 inflammasome expression and phosphorylated p38mitogen-activated protein kinase levels which correlated with the NLRP3 inflammasome, the UPR effector ATF4, and total tau levels. Trazodone reduced theta oscillations during REM sleep and enhanced rapid eye movement (REM) sleep duration. Olfactory memory transiently improved, and memory performance correlated with REM sleep duration and theta oscillations. These findings on the effects of trazodone on the NLRP3 inflammasome, the unfolded protein response and behavioural hallmarks of dementia warrant further studies on the therapeutic value of sleep-modulating compounds for tauopathies.
Introduction: Accurate and rapid diagnostics paired with effective tracking and tracing systems are key to halting the spread of infectious diseases, limiting the emergence of new variants and to monitor vaccine efficacy. The current gold standard test (RT-qPCR) for COVID-19 is highly accurate and sensitive, but is time-consuming, and requires expensive specialised, lab-based equipment. Methods: Herein, we report on the development of a SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) rapid and inexpensive diagnostic platform that relies on a reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) assay and a portable smart diagnostic device. Automated image acquisition and an Artificial Intelligence (AI) deep learning model embedded in the Virus Hunter 6 (VH6) device allow to remove any subjectivity in the interpretation of results. The VH6 device is also linked to a smartphone companion application that registers patients for swab collection and manages the entire process, thus ensuring tests are traced and data securely stored. Results: Our designed AI-implemented diagnostic platform recognises the nucleocapsid protein gene of SARS-CoV-2 with high analytical sensitivity and specificity. A total of 752 NHS patient samples, 367 confirmed positives for coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and 385 negatives, were used for the development and validation of the test and the AI-assisted platform. The smart diagnostic platform was then used to test 150 positive clinical samples covering a dynamic range of clinically meaningful viral loads and 250 negative samples. When compared to RT-qPCR, our AI-assisted diagnostics platform was shown to be reliable, highly specific (100%) and sensitive (98–100% depending on viral load) with a limit of detection of 1.4 copies of RNA per µL in 30 min. Using this data, our CE-IVD and MHRA approved test and associated diagnostic platform has been approved for medical use in the United Kingdom under the UK Health Security Agency’s Medical Devices (Coronavirus Test Device Approvals, CTDA) Regulations 2022. Laboratory and in-silico data presented here also indicates that the VIDIIA diagnostic platform is able to detect the main variants of concern in the United Kingdom (September 2023). Discussion: This system could provide an efficient, time and cost-effective platform to diagnose SARS-CoV-2 and other infectious diseases in resource-limited settings.
The role of m6A methylation of RNA has remained elusive for decades, however recent technological advances are now allowing the mapping of the m6A methylation landscape at nucleotide level. This has spurred an explosion in our understanding of the role played by RNA epigenetics in RNA biology. m6A modifications have been tied to almost every aspects of the mRNA life cycle and it is now clear that RNA virus genomes are subject to m6A methylation. These modifications play various roles in the viral replication cycle. This review will summarize recent breakthroughs concerning m6A RNA modification and their implications for cellular and viral RNAs.
In this review, we provide an overview of the strategies developed by caliciviruses to subvert or regulate the host protein synthesis machinery to their advantage. As intracellular obligate parasites, viruses strictly depend on the host cell resources to produce viral proteins. Thus, many viruses have developed strategies that regulate the function of the host protein synthesis machinery, often leading to preferential translation of viral mRNAs. Caliciviruses lack a 5′ cap structure but instead have a virus-encoded VPg protein covalently linked to the 5′ end of their mRNAs. Furthermore, they encode 2–4 open reading frames within their genomic and subgenomic RNAs. Therefore, they use alternative mechanisms for translation whereby VPg interacts with eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs) to act as a proteinaceous cap-substitute, and some structural proteins are produced by reinitiation of translation events. This review discusses our understanding of these key mechanisms during caliciviruses infection as well as recent insights into the global regulation of eIF4E activity.
As obligate parasites, viruses strictly depend on host cell translation for the production of new progeny, yet infected cells also synthesize antiviral proteins to limit virus infection. Modulation of host cell translation therefore represents a frequent strategy by which viruses optimize their replication and spread. Here we sought to define how host cell translation is regulated during infection of human cells with Dengue Virus (DENV) and Zika Virus (ZIKV), two positive-strand RNA flaviviruses. Polysome profiling and analysis of de novo protein synthesis revealed that flavivirus infection causes potent repression of host cell translation while synthesis of viral proteins remains efficient. Selective repression of host cell translation was mediated by the DENV polyprotein at the level of translation initiation. In addition, DENV and ZIKV infection suppressed host cell stress responses such as the formation of stress granules and phosphorylation of the translation initiation factor eIF2α. Mechanistic analyses revealed that translation repression was uncoupled from the disruption of stress granule formation and eIF2α signaling. Rather, DENV infection induced p38-Mnk1 signaling that resulted in the phosphorylation of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4E and was essential for the efficient production of virus particles. Together, these results identify the uncoupling of translation suppression from the cellular stress responses as a conserved strategy by which flaviviruses ensure efficient replication in human cells.
Alphaviruses have positive-strand RNA genomes containing two open reading frames (ORFs). The first ORF encodes the nonstructural (ns) polyproteins P123 and P1234 that act as precursors for the subunits of the viral RNA replicase (nsP1 to nsP4). Processing of P1234 leads to the formation of a negative-strand replicase consisting of nsP4 (RNA polymerase) and P123 components. Subsequent processing of P123 results in a positive-strand replicase. The second ORF encoding the structural proteins is expressed via the synthesis of a subgenomic RNA. Alphavirus replicase is capable of using template RNAs that contain essential cis-active sequences. Here, we demonstrate that the replicases of nine alphaviruses, expressed in the form of separate P123 and nsP4 components, are active. Their activity depends on the abundance of nsP4. The match of nsP4 to its template strongly influences efficient subgenomic RNA synthesis. nsP4 of Barmah Forest virus (BFV) formed a functional replicase only with matching P123, while nsP4s of other alphaviruses were compatible also with several heterologous P123s. The P123 components of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus and Sindbis virus (SINV) required matching nsP4s, while P123 of other viruses could form active replicases with different nsP4s. Chimeras of Semliki Forest virus, harboring the nsP4 of chikungunya virus, Ross River virus, BFV, or SINV were viable. In contrast, chimeras of SINV, harboring an nsP4 from different alphaviruses, exhibited a temperature-sensitive phenotype. These findings highlight the possibility for formation of new alphaviruses via recombination events and provide a novel approach for the development of attenuated chimeric viruses for vaccination strategies. IMPORTANCE A key element of every virus with an RNA genome is the RNA replicase. Understanding the principles of RNA replicase formation and functioning is therefore crucial for understanding and responding to the emergence of new viruses. Reconstruction of the replicases of nine alphaviruses from nsP4 and P123 polyproteins revealed that the nsP4 of the majority of alphaviruses, including the mosquito-specific Eilat virus, could form a functional replicase with P123 originating from a different virus, and the corresponding chimeric viruses were replication-competent. nsP4 also had an evident role in determining the template RNA preference and the efficiency of RNA synthesis. The revealed broad picture of the compatibility of the replicase components of alphaviruses is important for understanding the formation and functioning of the alphavirus RNA replicase and highlights the possibilities for recombination between different alphavirus species.
In response to stress such as virus infection, cells can stall translation by storing mRNAs away in cellular compartments called stress granules (SGs). This defence mechanism favours cell survival by limiting the use of energy and nutrients until the stress is resolved. In some cases it may also block viral propagation as viruses are dependent on the host cell resources to produce viral proteins. Human norovirus is a member of the Caliciviridae family responsible for gastroenteritis outbreaks worldwide. Previous studies on caliciviruses have identified mechanisms by which they can usurp the host translational machinery, using the viral protein genome-linked VPg, or regulate host protein synthesis through the MAPK pathway. Herein we examined the effect of feline calicivirus (FCV) infection on SGs accumulation. We show that FCV infection impairs the assembly of SGs despite an increased phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF2α, a hallmark of stress pathway activation. Furthermore SGs did not accumulate in FCV-infected cells that are stressed with arsenite or hydrogen peroxide. FCV infection resulted in the cleavage of the SG-nucleating protein Ras-GTPase activating SH3 domain-binding protein (G3BP1), which is mediated by the viral 3C-like proteinase NS6Pro 38 . Using mutational analysis, we identified the FCV-induced cleavage site within G3BP1, which differs from the poliovirus 3C proteinase cleavage site previously identified. Finally, we showed that NS6Pro 41 -mediated G3BP1 cleavage impairs SGs assembly. In contrast, murine norovirus (MNV) infection did not impact arsenite-induced SG assembly or G3BP1 integrity suggesting that related caliciviruses have distinct effects on the stress response pathway.
Equine hepacivirus (EHcV) (now also classified as hepacivirus A) is the closest genetic relative to hepatitis C virus (HCV) and is proposed to have diverged from HCV within the last 1000 years. The 5′ untranslated regions (UTRs) of both HCV and EHcV exhibit internal ribosome entry site (IRES) activity, allowing cap-independent translational initiation, yet only the HCV 5′UTR has been systematically analysed. Here, we report a detailed structural and functional analysis of the EHcV 5′UTR. The secondary structure was determined using selective 2′ hydroxyl acylation analysed by primer extension (SHAPE), revealing four stem–loops, termed SLI, SLIA, SLII and SLIII, by analogy to HCV. This guided a mutational analysis of the EHcV 5′UTR, allowing us to investigate the roles of the stem–loops in IRES function. This approach revealed that SLI was not required for EHcV IRES-mediated translation. Conversely, SLIII was essential, specifically SLIIIb, SLIIId and a GGG motif that is conserved across the Hepaciviridae. Further SHAPE analysis provided evidence that this GGG motif mediated interaction with the 40S ribosomal subunit, whilst a CUU sequence in the apical loop of SLIIIb mediated an interaction with eIF3. In addition, we showed that a microRNA122 target sequence located between SLIA and SLII mediated an enhancement of translation in the context of a subgenomic replicon. Taken together, these results highlight the conservation of hepaciviral translation mechanisms, despite divergent primary sequences.
Viral infections impose major stress on the host cell. In response, stress pathways can rapidly deploy defence mechanisms by shutting off the protein synthesis machinery and triggering the accumulation of mRNAs into stress granules to limit the use of energy and nutrients. Because this threatens viral gene expression, viruses need to evade these pathways to propagate. Human norovirus is responsible for gastroenteritis outbreaks worldwide. Here we examined how norovirus interacts with the eIF2α signaling axis controlling translation and stress granules. While norovirus infection represses host cell translation, our mechanistic analyses revealed that eIF2α signaling mediated by the stress kinase GCN2 is uncoupled from translational stalling. Moreover, infection results in a redistribution of the RNA-binding protein G3BP1 to replication complexes and remodelling of its interacting partners, allowing the avoidance from canonical stress granules. These results define novel strategies by which norovirus undergo efficient replication whilst avoiding the host stress response and manipulating the G3BP1 interactome.
Viruses must hijack cellular translation machinery to express viral genes. In many cases, this is impeded by cellular stress responses. These stress responses result in the global inhibition of translation and the storage of stalled mRNAs, into RNA-protein aggregates called stress granules. This results in the translational silencing of the majority of mRNAs excluding those beneficial for the cell to resolve the specific stress. For example, the expression of antiviral factors is maintained during viral infection. Here we investigated stress granule regulation by Gammacoronavirus infectious bronchitis virus (IBV), which causes the economically important poultry disease, infectious bronchitis. Interestingly, we found that IBV is able to inhibit multiple cellular stress granule signaling pathways, whilst at the same time, IBV replication also results in the induction of seemingly canonical stress granules in a proportion of infected cells. Moreover, IBV infection uncouples translational repression and stress granule formation and both processes are independent of eIF2 alpha phosphorylation. These results provide novel insights into how IBV modulates cellular translation and antiviral stress signaling.
Stress granules (SGs) are membrane-less organelles that assemble in the cytoplasm to organize cellular contents and promote rapid adaptation during stress. To understand how SGs contribute to physiological functions, we used electrochemical measurements to detect electroactive species in SGs. With amperometry, we discovered that reactive oxygen species (ROS) are encapsulated inside arsenite-induced SGs, and H2O2 is the main species. The release kinetics of H2O2 from single SGs and the number of H2O2 molecules were quantified. The discovery that SGs contain ROS implicates them as communicators of the cellular stresses rather than a simple endpoint. This may explain how SGs regulate cellular metabolism and stress responses. This may also help better understand their cytoprotective functions in pathological conditions associated with SGs such as neurodegenerative diseases (NDs), cancers and viral infections.
The accuracy of start codon selection is determined by the translation initiation process. In prokaryotes the initiation step on most mRNAs relies on recruitment of the small ribosomal subunit onto the initiation codon by base pairing between the mRNA and the 16S rRNA. Eukaryotes have evolved a complex molecular machinery involving at least 11 initiation factors, and mRNAs do not directly recruit the small ribosomal subunit. Instead the initiation complex is recruited to the 5' end of the mRNA through a complex protein network including eIF4E that interacts with the 5' cap structure and poly-A binding protein that interacts with the 3'end. However, some viral and cellular mRNAs are able to escape this pathway by internal recruitment of one or several components of the translation machinery. Here we review those eukaryotic mRNAs that have been reported to directly recruit the 40S ribosomal subunit internally. In the well characterized cases of viral IRESes, a specific RNA structure is involved in this process, and in addition to recruitment of the ribosome, the mRNA also manipulates the ribosome structure to stimulate the first translocation step. We also review recently described IRES/ribosome interactions in cases where the molecular mechanism leading to translation initiation has yet to be described. Finally we evaluate the possibility that mRNA may recruit the 40S ribosomal subunit through base pairing with the 18S rRNA.
An important feature of Mycobacterium tuberculosis pathogenesis is the ability to control cell death in infected host cells, including inhibition of apoptosis and stimulation of necrosis. Recently an alternative form of programmed cell death, necroptosis, has been described where necrotic cell death is induced by apoptotic stimuli under conditions where apoptotic execution is inhibited. We show for the first time that M. tuberculosis and TNFα synergise to induce necroptosis in murine fibroblasts via RIPK1-dependent mechanisms and characterized by phosphorylation of Ser345 of the MLKL necroptosis death effector. However, in murine macrophages M. tuberculosis and TNFα induce non-necroptotic cell death that is RIPK1-dependent but independent of MLKL phosphorylation. Instead, M. tuberculosis-infected macrophages undergo RIPK3-dependent cell death which occurs both in the presence and absence of TNFα and involves the production of mitochondrial ROS. Immunocytochemical staining for MLKL phosphorylation further demonstrated the occurrence of necroptosis in vivo in murine M. tuberculosis granulomas. Phosphorylated- MLKL immunoreactivity was observed associated with the cytoplasm and nucleus of fusiform cells in M. tuberculosis lesions but not in proximal macrophages. Thus whereas pMLKL-driven necroptosis does not appear to be a feature of M. tuberculosis-infected macrophage cell death, it may contribute to TNFα-induced cytotoxicity of the lung stroma and therefore contribute to necrotic cavitation and bacterial dissemination.
N6-Methyladenosine (m6A), the most abundant posttranscriptional messenger RNA (mRNA) modification, is emerging as an important regulator of gene expression1. Manipulation of m6A impacts different developmental and biological processes, and altered m6A homeostasis is linked to cancer2-5. m6A is catalyzed by METTL3 and enriched in the 3’ untranslated region (3’ UTR) of a large subset of mRNAs at sites close to the stop codon1. METTL3 can promote translation but the mechanism and widespread relevance remain unknown2. Here we show that METTL3 enhances translation only when tethered to reporter mRNA at sites close to the stop codon supporting a mRNA looping mechanism for ribosome recycling and translational control. Electron microscopy reveals the topology of individual polyribosomes with single METTL3 foci found in close proximity to 5’ cap-binding proteins. We identify a direct physical and functional interaction between METTL3 and the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit h (eIF3h). METTL3 promotes translation of a large subset of oncogenic mRNAs, including Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) that are also m6A-modified in human primary lung tumors. The METTL3-eIF3h interaction is required for enhanced translation, formation of densely packed polyribosomes, and oncogenic transformation. METTL3 depletion inhibits tumorigenicity and sensitizes lung cancer cells to BRD4 inhibition. These findings uncover a mRNA looping mechanism of translation control and identify METTL3-eIF3h as a potential cancer therapeutic target.
The RNA genome of Seneca Valley virus (SVV), a recently identified picornavirus, contains an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) element which has structural and functional similarity to that from classical swine fever virus (CSFV) and hepatitis C virus, members of the Flaviviridae. The SVV IRES has an absolute requirement for the presence of a short region of virus-coding sequence to allow it to function either in cells or in rabbit reticulocyte lysate. The IRES activity does not require the translation initiation factor eIF4A or intact eIF4G. The predicted secondary structure indicates that the SVV IRES is more closely related to the CSFV IRES, including the presence of a bipartite IIId domain. Mutagenesis of the SVV IRES, coupled to functional assays, support the core elements of the IRES structure model, but surprisingly, deletion of the conserved IIId(2) domain had no effect on IRES activity, including 40S and eIF3 binding. This is the first example of a picornavirus IRES that is most closely related to the CSFV IRES and suggests the possibility of multiple, independent recombination events between the genomes of the Picornaviridae and Flaviviridae to give rise to similar IRES elements.
Translation initiation on HIV genomic RNA relies on both cap and Internal Ribosome Entry Site (IRES) dependant mechanisms that are regulated throughout the cell cycle. During a unique phenomenon, the virus recruits initiation complexes through RNA structures located within Gag coding sequence, downstream of the initiation codon. We analyzed initiation complexes paused on the HIV-2 gag IRES and revealed that they contain all the canonical initiation factors except eIF4E and eIF1. We report that eIF3 and the small ribosomal subunit bind HIV RNA within gag open reading frame. We thus propose a novel two step model whereby the initial event is the formation of a ternary eIF3/40S/IRES complex. In a second step, dependent on most of the canonical initiation factors, the complex is rearranged to transfer the ribosome on the initiation codons. The absolute requirement of this large structure for HIV translation defines a new function for a coding region. Moreover, the level of information compaction within this viral genome reveals an additional level of evolutionary constraint on the coding sequence. The conservation of this IRES and its properties in rapidly evolving viruses suggest an important role in the virus life cycle and highlight an attractive new therapeutic target.
Rapid, reliable, sensitive, portable, and accurate diagnostics are required to control disease outbreaks such as COVID-19 that pose an immense burden on human health and the global economy. Here we developed a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)-based electrochemical test for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 that causes COVID-19. The test is based on the oxidation-reduction reaction between pyrophosphates (generated from positive LAMP reaction) and molybdate that is detected by cyclic voltammetry using inexpensive and disposable carbon screen printed electrodes. Our test showed higher sensitivity (detecting as low as 5.29 RNA copies/μL) compared to the conventional fluorescent reverse transcriptase (RT)-LAMP. We validated our tests using human serum and saliva spiked with SARS-CoV-2 RNA and clinical (saliva and nasal-pharyngeal) swab samples demonstrating 100% specificity and 93.33% sensitivity. Our assay provides a rapid, specific, and sensitive test with an electrochemical readout in less than 45 min that could be adapted for point-of-care settings.
We are just beginning to unravel the myriad of interactions in which non-coding RNAs participate. The intricate RNA interactome is the foundation of many biological processes, including bacterial virulence and human disease, and represents unexploited resources for the development of potential therapeutic interventions. However, identifying specific associations of a given RNA from the multitude of possible binding partners within the cell requires robust high-throughput systems for their rapid screening. Here, we present the first demonstration of functional-RNA arrays as a novel platform technology designed for the study of such interactions using immobilized, active RNAs. We have generated high-density RNA arrays by an innovative method involving surface-capture of in vitro transcribed RNAs. This approach has significant advantages over existing technologies, particularly in its versatility in regards to binding partner character. Indeed, proof-of-principle application of RNA arrays to both RNA–small molecule and RNA–RNA pairings is demonstrated, highlighting their potential as a platform technology for mapping RNA-based networks and for pharmaceutical screening. Furthermore, the simplicity of the method supports greater user-accessibility over currently available technologies. We anticipate that functional-RNA arrays will find broad utility in the expanding field of RNA characterization.
Obscurins are large filamentous proteins with crucial roles in the assembly, stability and regulation of muscle. Characteristic of these proteins is a tandem of two C-terminal kinase domains, PK1 and PK2, that are separated by a long intrinsically disordered sequence. The significance of this conserved domain arrangement is unknown. Our study of PK1 from Drosophila obscurin shows that this is a pseudokinase with features typical of the CAM-kinase family, but which carries a minimalistic regulatory tail that no longer binds calmodulin or has mechanosensory properties typical of other sarcomeric kinases. PK1 binds ATP with high affinity, but in the absence of magnesium and lacks detectable phosphotransfer activity. It also has a highly diverged active site, strictly conserved across arthropods, that might have evolved to accommodate an unconventional binder. We find that PK1 interacts with PK2, suggesting a functional relation to the latter. These findings lead us to speculate that PK1/PK2 form a pseudokinase/kinase dual system, where PK1 might act as an allosteric regulator of PK2 and where mechanosensing properties, akin to those described for regulatory tails in titin-like kinases, might now reside on the unstructured interkinase segment. We propose that the PK1-interkinase-PK2 region constitutes an integrated functional unit in obscurin proteins.
Subunit viral vaccines are typically not as efficient as live attenuated or inactivated vaccines at inducing protective immune responses. This paper describes an alternative ‘biomimetic’ technology; whereby viral antigens were formulated around a polymeric shell in a rationally arranged fashion with a surface glycoprotein coated on to the surface and non-structural antigen and adjuvant encapsulated. We evaluated this model using BVDV E2 and NS3 proteins formulated in poly-(D, L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticles adjuvanted with polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid (poly(I:C) as an adjuvant (Vaccine-NP). This Vaccine-NP was compared to ovalbumin and poly(I:C) formulated in a similar manner (Control-NP) and a commercial adjuvanted inactivated BVDV vaccine (IAV), all inoculated subcutaneously and boosted prior to BVDV-1 challenge. Significant virus-neutralizing activity, and E2 and NS3 specific antibodies were observed in both Vaccine-NP and IAV groups following the booster immunisation. IFN-γ responses were observed in ex vivo PBMC stimulated with E2 and NS3 proteins in both vaccinated groups. We observed that the protection afforded by the particulate vaccine was comparable to the licenced IAV formulation. In conclusion, the biomimetic particulates showed a promising immunogenicity and efficacy profile that may be improved by virtue of being a customisable mode of delivery.
Stress granules (SGs) are stress-induced biomolecular condensates which originate primarily from inactivated RNA translation machinery and translation initiation factors. SG formation is an important defensive mechanism for cell survival, while its dysfunction has been linked to neurodegenerative diseases. However, the molecular mechanisms of SG assembly and disassembly, as well as their impacts on cellular recovery, are not fully understood. More thorough investigations into the molecular dynamics of SG pathways are required to understand the pathophysiological roles of SGs in cellular systems. Here, we characterize the SG and cytoplasmic protein turnover in neuronal progenitor cells (NPCs) under stressed and non-stressed conditions using correlative STED and NanoSIMS imaging. We incubate NPCs with isotopically labelled ( N) leucine and stress them with the ER stressor thapsigargin (TG). A correlation of STED and NanoSIMS allows the localization of individual SGs (using STED), and their protein turnover can then be extracted based on the N/ N ratio (using NanoSIMS). We found that TG-induced SGs, which are highly dynamic domains, recruit their constituents predominantly from the cytoplasm. Moreover, ER stress impairs the total cellular protein turnover regimen, and this impairment is not restored after the commonly proceeded stress recovery period.
Translation initiation on HIV genomic RNA relies on both cap and Internal Ribosome Entry Site (IRES) dependant mechanisms that are regulated throughout the cell cycle. During a unique phenomenon, the virus recruits initiation complexes through RNA structures located within Gag coding sequence, downstream of the initiation codon. We analyzed initiation complexes paused on the HIV-2 gag IRES and revealed that they contain all the canonical initiation factors except eIF4E and eIF1. We report that eIF3 and the small ribosomal subunit bind HIV RNA within gag open reading frame. We thus propose a novel two step model whereby the initial event is the formation of a ternary eIF3/40S/IRES complex. In a second step, dependent on most of the canonical initiation factors, the complex is rearranged to transfer the ribosome on the initiation codons. The absolute requirement of this large structure for HIV translation defines a new function for a coding region. Moreover, the level of information compaction within this viral genome reveals an additional level of evolutionary constraint on the coding sequence. The conservation of this IRES and its properties in rapidly evolving viruses suggest an important role in the virus life cycle and highlight an attractive new therapeutic target.
Atypical ruminant pestiviruses are closely related to the two bovine viral diarrhoea virus (BVDV) species, BVDV-1 and BVDV-2. While there is evidence of cross-protective immune responses between BVDV-1 and BVDV-2, despite antigenic differences, there is little information on the antigenic cross-reactivity with atypical ruminant pestiviruses. The aim of this study was therefore to assess the specificity of antibody and T cell responses induced by experimental infection of calves with BVDV-1 strain Ho916, Th/04_KhonKaen (TKK), an Asiatic atypical ruminant pestivirus, or co-infection with both viruses. Homologous virus neutralization was observed in sera from both single virus infected and co-infected groups, while cross-neutralization was only observed in the TKK infected group. T cell IFN-γ responses to both viruses were observed in the TKK infected animals, whereas Ho916 infected calves responded better to homologous virus. Specifically, IFN-γ responses to viral non-structural protein, NS3, were observed in all infected groups while responses to viral glycoprotein, E2, were virus-specific. Broader antigen-specific cytokine responses were observed with similar trends between inoculation groups and virus species. The limited T cell and antibody immune reactivity of Ho916 inoculated animals to TKK suggests that animals vaccinated with current BVDV-1-based vaccines may not be protected against atypical ruminant pestiviruses.
Viral internal ribosomes entry site (IRES) elements coordinate the recruitment of the host translation machinery to direct the initiation of viral protein synthesis. Within hepatitis C virus (HCV)-like IRES elements, the sub-domain IIId(1) is crucial for recruiting the 40S ribosomal subunit. However, some HCV-like IRES elements possess an additional sub-domain, termed IIId2, whose function remains unclear. Herein we show that IIId2 sub-domains from divergent viruses have different functions. The IIId2 sub-domain present in Seneca valley virus (SVV), a picornavirus, is dispensable for IRES activity, while the IIId2 sub-domains of two pestiviruses, classical swine fever virus (CSFV) and border disease virus (BDV), are required for 80S ribosomes assembly and IRES activity. Unlike in SVV, the deletion of IIId2 from the CSFV and BDV IRES elements impairs initiation of translation by inhibiting the assembly of 80S ribosomes. Consequently, this negatively affects the replication of CSFV and BDV. Finally, we show that the SVV IIId2 sub-domain is required for efficient viral RNA synthesis and growth of SVV, but not for IRES function. This study sheds light on the molecular evolution of viruses by clearly demonstrating that conserved RNA structures, within distantly related RNA viruses, have acquired different roles in the virus life cycles.
Enterovirus 71 (EV71) is associated with severe neurological disorders in children, and has been implicated as the infectious agent in several large-scale outbreaks with mortalities. Upon infection, the viral RNA is translated in a cap-independent manner to yield a large polyprotein precursor. This mechanism relies on the presence of an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) element within the 5'-untranslated region. Virus-host interactions in EV71-infected cells are crucial in assisting this process. We identified a novel positive IRES trans-acting factor, far upstream element binding protein 1 (FBP1). Using binding assays, we mapped the RNA determinants within the EV71 IRES responsible for FBP1 binding and mapped the protein domains involved in this interaction. We also demonstrated that during EV71 infection, the nuclear protein FBP1 is enriched in cytoplasm where viral replication occurs. Moreover, we showed that FBP1 acts as a positive regulator of EV71 replication by competing with negative ITAF for EV71 IRES binding. These new findings may provide a route to new anti-viral therapy.
Equine infectious anaemia virus (EIAV) is a retrovirus with worldwide distribution which is notifiable to the OIE. Despite its importance to the equine industry, most information regarding its biology have been obtained using only two strains (EIAVWYO and EIAVLIA) from the USA and China, respectively. Recently full genome sequences from Ireland, Italy and Japan have been published; however, this is still not representative of the number of EIAV outbreaks experienced globally each year. The limited availability of published sequences makes design of a universal EIAV PCR difficult, hence diagnosis is solely reliant on serology. Accordingly, it is important to further investigate the re‐emerging cases in other areas of the world. Here, we provide information regarding the outbreaks of EIA in England in 2010 and 2012 including the molecular characterization of strains. Full genome was obtained for two symptomatic cases but could not be resolved for the asymptomatic cases. The two British genomes from 2010 (EIAVDEV) and 2012 (EIAVCOR) each represent a new phylogenetic group, each differing genetically from the other available full genome sequences by 21.1%–25.5%. That the majority of new EIAV full genome sequences to be published adds another phylogenetic group indicates that the surface of EIAV global diversity is just being scratched. These data highlight that further work is needed to fully understand EIAV genetic diversity, namely the full genome sequencing of EIAV cases from a variety of locations and time points. This would aid both the use of phylogenetics in parallel with horse tracing as the epidemiological tool of disease tracking and the design of a universally applicable molecular diagnostic method.
Noroviruses produce viral RNAs lacking a 5’ cap structure and instead use a virus-encoded VPg protein covalently linked to viral RNA to interact with translation initiation factors and drive viral protein synthesis. Norovirus infection results in the induction of the innate response leading to interferon stimulated gene (ISG) transcription. However the translation of the induced ISG mRNAs is suppressed. A SILAC-based mass spectrometry approach was employed to analyse changes to protein abundance in both whole cell and m7GTP-enriched samples to demonstrate that diminished host mRNA translation correlates with changes to the composition of the eukaryotic initiation factor complex. The suppression of host ISG translation correlates with the activity of the viral protease (NS6) and the activation of cellular caspases leading to the establishment of an apoptotic environment. These results indicate that noroviruses exploit the differences between viral VPg-dependent and cellular cap-dependent translation in order to diminish the host response to infection.
Ribopuromycylation enables the visualization and quantitation of translation on a cellular level by immunofluorescence or in total using standard western blotting. This technique uses ribosome catalyzed puromycylation of nascent chains followed by immobilization on the ribosome by antibiotic chain elongation inhibitor emetine. Detection of puromycylated ribosome-bound nascent chains can then be achieved using a puromycin-specific antibody.
Members of the Flaviviridae family, including dengue virus (DENV) and yellow fever virus, cause serious disease in humans, whilst maternal infection with Zika virus (ZIKV) can induce microcephaly in newborns. Following infection, flaviviral RNA genomes are translated to produce the viral replication machinery but must then serve as a template for the transcription of new genomes. However, the ribosome and viral polymerase proceed in opposite directions along the RNA, risking collisions and abortive replication. Whilst generally linear, flavivirus genomes can adopt a circular conformation facilitated by long-range RNA–RNA interactions, shown to be essential for replication. Using an in vitro reconstitution approach, we demonstrate that circularization inhibits de novo translation initiation on ZIKV and DENV RNA, whilst the linear conformation is translation-competent. Our results provide a mechanism to clear the viral RNA of ribosomes in order to promote efficient replication and, therefore, define opposing roles for linear and circular conformations of the flavivirus genome.
Knowledge of the host factors required for norovirus replication has been hindered by the challenges associated with culturing human noroviruses. We have combined proteomic analysis of the viral translation and replication complexes with a CRISPR screen, to identify host factors required for norovirus infection. The core stress granule component G3BP1 was identified as a host factor essential for efficient human and murine norovirus infection, demonstrating a conserved function across the Norovirus genus. Furthermore, we show that G3BP1 functions in the novel paradigm of viral VPg-dependent translation initiation, contributing to the assembly of translation complexes on the VPg-linked viral positive sense RNA genome by facilitating ribosome recruitment. Our data uncovers a novel function for G3BP1 in the life cycle of positive sense RNA viruses and identifies the first host factor with pan-norovirus pro-viral activity.
Additional publications
• Easton LE, Locker N and Lukavsky PJ (2009) Conserved functional domains and a novel tertiary interaction near the pseudoknot drive translational activity of hepatitis C virus and hepatitis C virus-like internal ribosome entry sites. Nucleic Acids Research.
• Locker N, Easton LE and Lukavsky PJ (2007) HCV and CSFV IRES domain II mediate eIF2 release during 80S ribosome assembly. EMBO Journal, 26: 795-805.
• ElAntak L, Tzakos AG, Locker N and Lukavsky PJ (2007) Structure of eIF3b-RRM and its interaction with eIF3j, structural insights into the recruitment of eIF3 to the 40S ribosomal subunit. Journal of Biochemical Chemistry, 282: 8165-74.
• Locker N and Lukavsky PJ (2007) A practical approach to isolate 48S complexes: Affinity purification and analyses. Methods in Enzymology, 429 :83-104.
• Locker N, Easton LE and Lukavsky PJ (2006) Affinity purification of eukaryotic 48S initiation complexes. RNA, 12: 683-690.
• Hallay H§, Locker N§, Ayadi L, Ropers D, Guittet E and Branlant C (2006) Biochemical and NMR study on the competition between proteins SC35 Srp40 and hnRNP A1 at the HIV-1 tat exon 2 splicing site. Journal of Biochemical Chemistry, 281: 37159-37174.