Dr Jing Zhang
Academic and research departments
Advanced Technology Institute, Faculty of Engineering and Physical Sciences.Publications
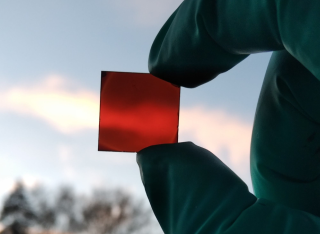
•Flexible Zn-ion battery-powered PANI IR-ECDs with superior modulation properties are developed.•High Δε of 0.56 at 8‒14 μm and significant radiative temperature modulation of 10.9 °C are achieved at ~40 °C.•The device exhibits an extremely low Δε decay rate of 0.0145 % per cycle after 120,000 s continuous cycling.•Multifunctionalities such as self-powering, solar modulation compatibility, and multi-spectral camouflage are demonstrated. Electrochromic devices (ECDs) capable of modulating infrared emission hold great potential in many application fields, including energy harvesting and conservation, sustainable building technology, thermal imaging, and spacecraft thermal control. However, its wider implementation requires the development of innovative strategies to achieve high modulation ratio, high flexibility, low cost, and seamless integration capabilities. Here we present a low-cost, large-area-compatible, solution-process approach for flexible infrared ECDs (IR-ECDs) by designing gradient porous membrane-supported polyaniline (PANI) composite structures. These devices achieve a superior emissivity variation (Δε) of 0.56 across the critical atmospheric transparency window of 8–14, coupled with a large modulation of radiative temperature by 10.9 °C at 40 °C environmental conditions. Remarkably, they retain a high Δε even after 120,000 s of continuous operation, demonstrating exceptional cycling durability with a minimal emissivity decay rate of 0.0145 % per cycle. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the flexible, self-powered IR-ECDs are able to support continuous modulation operation for an impressive duration of circa 20 years for a large device with an area of 1 m2, consuming a minimal 1-kilowatt hour (kWh) of electricity. This development paves the way for new, high-efficiency strategies in preparing and deploying high-performance adaptive energy-management applications.
Incontrovertibly there is an increasing demand for the development of benign inks suitable for fabrication of high-performing perovskite-based thin film functional layers. Nevertheless, most reported perovskite precursors rely on the use of highly toxic solvents such as acetonitrile, 2-methoxyethanol, dimethylformamide, and many others. Hence, there is a strong imperative for the development of novel and greener inks, which will facilitate smoother commercialization of technologies based on functional perovskite films. Therefore, four perovskite precursors are studied, some of which consist of up to 90% ethanol. All inks are developed to fulfill the requirements of a high-throughput deposition compatible with roll-to-roll techniques at room temperature, assisted by an air knife for instant solvent removal. Two of the inks are particularly suitable for the fabrication of high-quality and densely packed multi-crystalline (CH3NH3)PbI3 layers, as confirmed by numerous nanoscale spectroscopic and material characterization techniques. Additionally, large-area photoluminescence (PL) imaging is demonstrated to improve the quality of the deposited perovskite films, with a route to enhance deposition uniformity when upscaling for manufacture. The genuine potential of the developed greener perovskite inks is demonstrated with the fabrication of solar cells with power conversion efficiencies above 19.5%.
In article number 2300564, Silva and co-workers demonstrate the development of green precursor inks suitable for the large-scale fabrication of high-quality perovskite films at room temperature. The inks can be used for the fabrication of different opto-electronic devices, i.e., perovskite solar cells, with efficiencies above 19.5%.
Miniaturized flexible photo-rechargeable systems show bright prospects for wide applications in internet of things, self-powered health monitoring and emergency electronics. However, conventional systems still suffer from complex manufacturing processes, slow photo-charging and discharging rate, and mismatch between photovoltaic and energy storage components in size, mechanics and voltage, etc. Here, we demonstrate a facile inkjet printing and electrodeposition approach for fabricating a highly integrated flexible photo-rechargeable system by combining stable and ultra-high-rate quasi-solid-state Zn-MnO2 micro-batteries (ZMBs) with flexible perovskite solar cells (FPSCs). In particular, Ni protective layer is first introduced into ZMBs to stabilize battery configuration and facilitate enhanced electrochemical performance. The optimized ZMB exhibits ultrahigh volumetric energy density of 148 mWh cm−3 (16.3 μWh cm−2) and power density of 55 W cm−3 (6.1 mW cm−2) at the current density of 400 C (5 mA cm−2), enabling them comparable with the state-of-the-art micro-batteries or supercapacitors fabricated by conventional methods. The embedded FPSCs show excellent photovoltaic performance, sufficient to charge ZMBs and create a self-charging system capable to offer energy autonomy in miniaturized wearable electronics. The integrated systems can achieve an ultrafast photo-charging within 30 s, with sufficient energy to power other functional electronics (e.g., LED bulb and pressure sensor) for tens of minutes. This prototype offers a promising scheme for next-generation miniaturized flexible photo-rechargeable systems.
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have emerged as a ‘rising star’ in recent years due to their high-power conversion efficiency (PCE), extremely low cost and facile fabrication techniques. To date, PSCs have achieved a certified PCE of 25.2% on rigid conductive substrates, and 19.5% on flexible substrates. The significant advancement of PSCs has been realized through various routes, including perovskite composition engineering, interface modification, surface passivation, fabrication process optimization, and exploitation of new charge transport materials. However, compared with rigid counterparts, the efficiency record of flexible perovskite solar cells (FPSCs) is advancing slowly, and therefore it is of great significance to scrutinize recent work and expedite the innovation in this field. In this article, we comprehensively review the recent progress of FPSCs. After a brief introduction, the major features of FPSCs are compared with other types of flexible solar cells in a broad context including silicon, CdTe, dye-sensitized, organic, quantum dot and hybrid solar cells. In particular, we highlight the major breakthroughs of FPSCs made in 2019/2020 for both laboratory and large-scale devices. The constituents of making a FPSC including flexible substrates, perovskite absorbers, charge transport materials, as well as device fabrication and encapsulation methods have been critically assessed. The existing challenges of making high performance and long-term stable FPSCs are discussed. Finally, we offer our perspectives on the future opportunities of FPSCs in the field of photovoltaics.
Bifacial perovskite solar cells have shown great promise for increasing power output by capturing light from both sides. However, the suboptimal optical transmittance of back metal electrodes together with the complex fabrication process associated with front transparent conducting oxides have hindered the development of efficient bifacial PSCs. Here, we present a novel approach for bifacial perovskite devices using single-walled carbon nanotubes as both front and back electrodes. single-walled carbon nanotubes offer high transparency, conductivity, and stability, enabling bifacial PSCs with a bifaciality factor of over 98% and a power generation density of over 36%. We also fabricate flexible, all-carbon-electrode-based devices with a high power-per-weight value of 73.75 W g-1 and excellent mechanical durability. Furthermore, we show that our bifacial devices have a much lower material cost than conventional monofacial PSCs. Our work demonstrates the potential of SWCNT electrodes for efficient, stable, and low-cost bifacial perovskite photovoltaics. The suboptimal optical transmittance of back electrodes and complex fabrication process hindered development of bifacial perovskite solar cells. Here, authors apply single-walled carbon nanotubes as front and back electrodes, achieving power generation density of 36% and bifaciality factor of 98%.
The unprecedented advancement in power conversion efficiencies (PCEs) of perovskite solar cells (PSCs) has rendered them a promising game-changer in photovoltaics. However, unsatisfactory environmental stability and high manufacturing cost of window electrodes are bottlenecks impeding their commercialization. Here, a strategy is introduced to address these bottlenecks by replacing the costly indium tin oxide (ITO) window electrodes via a simple transfer technique with single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) films, which are made of earth-abundant elements with superior chemical and environmental stability. The resultant devices exhibit PCEs of ≈19% on rigid substrates, which is the highest value reported to date for ITO-free PSCs. The facile approach for SWCNTs also enables application in flexible PSCs (f-PSCs), delivering a PCE of ≈18% with superior mechanical robustness over their ITO-based counterparts due to the excellent mechanical properties of SWCNTs. The SWCNT-based PSCs also deliver satisfactory performances on large-area (1 cm2 active area in this work). Furthermore, these SWCNT-based PSCs can retain over 80% of original PCEs after exposure to air over 700 h while ITO-based devices only sustain ≈60% of initial PCEs. This work paves a promising way to accelerate the commercialization of ITO-free PSCs with reduced material cost and prolonged lifetimes.
In this paper, we present a novel sequence design for efficient channel estimation in multiple input multiple output filterbank multicarrier (MIMO-FBMC) system with offset QAM modulation. Our proposed sequences, transmitted over one FBMC/OQAM symbol, are real-valued in the frequency domain and display zero-correlation zone properties in the time-domain. The latter property enables optimal channel estimation for a least-square estimator in frequency-selective fading channels. To further improve the system performance, we mitigate the data interference by an iterative feedback loop between channel estimation and FBMC demodulation. Simulation results validate that our proposed real-valued orthogonal sequences and the iterative channel estimation and demodulation scheme provide a practical solution for enhanced performance in preamble-based MIMO-FBMC systems.
Metal oxide charge transport materials are preferable for realizing long-term stable and potentially low-cost perovskite solar cells (PSCs). However, due to some technical difficulties (e.g., intricate fabrication protocols, high-temperature heating process, incompatible solvents, etc.), it is still challenging to achieve efficient and reliable all-metal-oxide-based devices. Here, we developed efficient inverted PSCs (IPSCs) based on solution-processed nickel oxide (NiOx) and tin oxide (SnO2) nanoparticles, working as hole and electron transport materials respectively, enabling a fast and balanced charge transfer for photogenerated charge carriers. Through further understanding and optimizing the perovskite/metal oxide interfaces, we have realized an outstanding power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 23.5% (the bandgap of the perovskite is 1.62 eV), which is the highest efficiency among IPSCs based on all-metal-oxide charge transport materials. Thanks to these stable metal oxides and improved interface properties, ambient stability (retaining 95% of initial PCE after 1 month), thermal stability (retaining 80% of initial PCE after 2 weeks) and light stability (retaining 90% of initial PCE after 1000 hours aging) of resultant devices are enhanced significantly. In addition, owing to the low-temperature fabrication procedures of the entire device, we have obtained a PCE of over 21% for flexible IPSCs with enhanced operational stability.
We report the direct determination of nonradiative lifetimes in Si/SiGe asymmetric quantum well structures designed to access spatially indirect (diagonal) interwell transitions between heavy-hole ground states, at photon energies below the optical phonon energy. We show both experimentally and theoretically, using a six-band k·p model and a time-domain rate equation scheme, that, for the interface quality currently achievable experimentally (with an average step height 1 greater than or equal to Å), interface roughness will dominate all other scattering processes up to about 200 K. By comparing our results obtained for two different structures we deduce that in this regime both barrier and well widths play an important role in the determination of the carrier lifetime. Comparison with recently published experimental and theoretical data obtained for mid-infrared GaAs/AlxGa1−xAs multiple quantum well systems leads us to the conclusion that the dominant role of interface roughness scattering at low temperature is a general feature of a wide range of semiconductor heterostructures not limited to IV-IV materials.
Producing an electrically pumped silicon-based laser at terahertz frequencies is gaining increased attention these days. This paper reviews the recent advances in the search for a silicon-based terahertz laser. Topics covered include resonant tunneling in p-type Si/SiGe, terahertz intersubband electroluminescence from quantum cascade structures, intersubband lifetime measurements in Si/SiGe quantum wells, enhanced optical guiding using buried silicide layers, and the potential for exploiting common impurity dopants in silicon such as boron and phosphorus to realize a terahertz laser
Grant-free non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) scheme is considered as a promising candidate for the enabling of massive connectivity and reduced signalling overhead for Internet of Things (IoT) applications in massive machine-type communication (mMTC) networks. Exploiting the inherent nature of sporadic transmissions in the grant-free NOMA systems, compressed sensing based multiuser detection (CS-MUD) has been deemed as a powerful solution to user activity detection (UAD) and data detection (DD). In this paper, block coordinate descend (BCD) method is employed in CS-MUD to reduce the computational complexity. We propose two modified BCD based algorithms, called enhanced BCD (EBCD) and complexity reduction enhanced BCD (CR-EBCD), respectively. To be specific, by incorporating a novel candidate set pruning mechanism into the original BCD framework, our proposed EBCD algorithm achieves remarkable CS-MUD performance improvement. In addition, the proposed CR-EBCD algorithm further ameliorates the proposed EBCD by eliminating the redundant matrix multiplications during the iteration process. As a consequence, compared with the proposed EBCD algorithm, our proposed CR-EBCD algorithm enjoys two orders of magnitude complexity saving without any CS-MUD performance degradation, rendering it a viable solution for future mMTC scenarios. Extensive simulation results demonstrate the bound-approaching performance as well as ultra-low computational complexity.
An efficient and robust video watermarking algorithm for the state-of-the-art video coding standard H.264/AVC is proposed for copyright protection. Grayscale 2-D watermark patterns such as detailed trademarks or logos can be highly compressed by a proposed grayscale watermark pre-processing, and inserted into the low bit-rate H.264/AVC videos in the compressed domain. The marked video sequences maintain good visual quality and the same overall consuming bit-rate. The proposed algorithm can robustly survive transcoding process and common signal processing, such as bit-rate reduction, Gaussian filtering and contrast enhancement.
N-channel enhancement mode Si/SiGe MOSFETs are characterised and studied over a wide temperature range of 10K
This paper investigates how the thermal diffusion of boron in silicon is influenced by a high energy fluorine implant with a dose in the range 5x10(14)-2.3x10(15) cm(-2). Secondary Ion Mass Spectroscopy (SIMS) profiles of boron marker layers are presented for different fluorine doses and compared with fluorine profiles to establish the conditions under which thermal boron diffusion is suppressed. The (SIMS) profiles show significantly reduced boron thermal diffusion above a critical F+ dose of 0.9-1.4x10(15) cm(-2). Fitting of the measured boron profiles gives suppressions of the boron thermal diffusion coefficient by factors of 1.9 and 3.7 for F+ implantation doses of 1.4x10(15) and 2.3x10(15) cm(-2), respectively. The suppression of boron thermal diffusion above the critical fluorine dose correlates with the appearance of a shallow fluorine peak on the (SIMS) profile in the vicinity of the boron marker layer. This shallow fluorine peak is present in samples with and without boron marker layers, and hence it is not due to a chemical interaction between the boron and the fluorine. Analysis of the (SIMS) profiles and cross-section Transmission Electron Microscope micrographs suggests that it is due to the trapping of fluorine at vacancy-fluorine clusters, and that the suppression of the boron thermal diffusion is due to the effect of the clusters in suppressing the interstitial concentration in the vicinity of the boron profile
Silicon-germanium (SiGe) heterojunction metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (SiGe HMOSFETs) have been successfully fabricated on Si substrate. The semiconductor heterostructure, which was grown by gas-source molecular beam epitaxy (GS-MBE), was initiated by the deposition of a Si Ge "virtual substrate". The n-type transistors were fabricated using a standard MOS process. The channel is a thin, undoped layer of strained Si and is buried below an arsenic-doped Si Ge layer, which provides the carriers. The devices exhibited excellent current-voltage (I-V) characteristics in terms of transconductance and drain current, with no breakdown or leakage. A level-1 model was extracted, for use in circuit design. The results suggest that the realisation of buried-channel SiGe n-HMOSFETs is feasible in MOS processes. These devices are of particular importance in analogue applications. © 2003 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
The role of oxygen concentration on the formation/evolution of residual defects in implanted and rapid thermal annealed silicon was studied in samples with various oxygen concentrations. Photoluminescence (PL) study showed a strong correlation between the D-line intensity and the oxygen concentration. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) measurements also suggested the extended defects were more favored in the high oxygen sample. High frequency capacitance-voltage (C-V) measurements revealed excess acceptors that were further investigated by deep level transient spectroscopy (DLTS). A hole trap with activation energy of 450 meV was detected and was suggested to relate to agglomerations of point defects associated with more than one type of 3D-metal related deep levels.